Comparing Tokenized Bonds vs. Traditional Bonds: Risks, Returns, and Accessibility

The debate around tokenized bonds vs traditional bonds is intensifying as institutional investors and forward-thinking asset managers weigh the transformative potential of blockchain in fixed income markets. At its core, a tokenized bond is a digital representation of a conventional debt instrument, issued and managed on blockchain infrastructure. This evolution promises not only to retain the essential features of bonds, principal, interest rate, and maturity, but also to unlock efficiencies that were previously unattainable in legacy financial systems.

Structural Differences: From Paperwork to Protocols
Traditional bonds have long relied on a complex web of intermediaries, from underwriters and custodians to clearinghouses and transfer agents. This multi-layered approach increases both issuance costs and settlement times, often stretching into days or even weeks. In contrast, tokenized bonds leverage blockchain’s distributed ledger technology to automate issuance, settlement, and record-keeping via smart contracts. This shift dramatically reduces paperwork, human error, and administrative overhead.
For example, while conventional bond settlements can require T and 2 or longer cycles, tokenized bonds enable near-instantaneous settlement, mitigating counterparty risk and freeing up capital for redeployment. According to InvestaX, this streamlined process not only accelerates market access but can also lower total issuance costs by eliminating redundant intermediaries.
Risks: Regulatory Uncertainty Meets Technological Innovation
No innovation comes without risk, and tokenizing fixed income is no exception. The most pressing concern remains regulatory uncertainty. While jurisdictions like Singapore and Switzerland are moving toward clearer frameworks for digital securities, many major markets are still grappling with how to classify and supervise these assets (source). Investors must navigate evolving compliance requirements that can impact everything from secondary trading eligibility to tax treatment.
Technological vulnerabilities also loom large. While blockchains offer robust security through decentralization and cryptography, smart contract bugs or protocol exploits could expose investors to new forms of operational risk. Additionally, market acceptance remains uneven; some institutional buyers remain cautious about adopting digital bond structures due to perceived complexity or lack of historical performance data.
Key Risks of Bond Tokens in 2025
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal framework for tokenized bonds remains in flux, with evolving rules and potential compliance challenges in major markets like the US and EU. Investors face ambiguity regarding investor protections, taxation, and cross-border transactions.
-

Technological Vulnerabilities: Tokenized bonds rely on blockchain platforms, exposing them to risks such as smart contract bugs, hacking, and cyberattacks. Even established blockchains like Ethereum have experienced high-profile exploits.
-
Market Acceptance Risk: Traditional investors and institutions may be hesitant to adopt tokenized bonds due to unfamiliarity and perceived operational risks, potentially limiting liquidity and price stability.
-
Platform and Counterparty Risk: Tokenized bonds are often issued and traded on specific digital platforms such as SIX Digital Exchange (SDX) or BondbloX Bond Exchange. Platform failures, insolvency, or technical issues could impact investor access and asset security.
-

Custody and Key Management: Investors must securely manage private keys or rely on third-party custodians. Loss or compromise of keys could result in permanent loss of assets, a risk not present in traditional bond custody systems.
Returns and Cost Efficiency: Can Digital Bonds Deliver More?
The promise of higher digital bond returns is rooted in cost efficiency. By automating manual processes and reducing reliance on intermediaries, tokenized bonds can lower both upfront issuance fees and ongoing transaction costs (InvestaX). These savings have the potential to be passed on in the form of higher yields for investors, though actual returns will always depend on issuer credit quality and prevailing market rates.
An additional benefit is faster settlement cycles through blockchain rails. Near-instantaneous transactions reduce counterparty exposure, a particularly valuable feature during volatile periods when every hour counts. However, it’s important for investors to balance these benefits against the possibility of illiquidity if secondary markets for specific tokens fail to develop robustly.
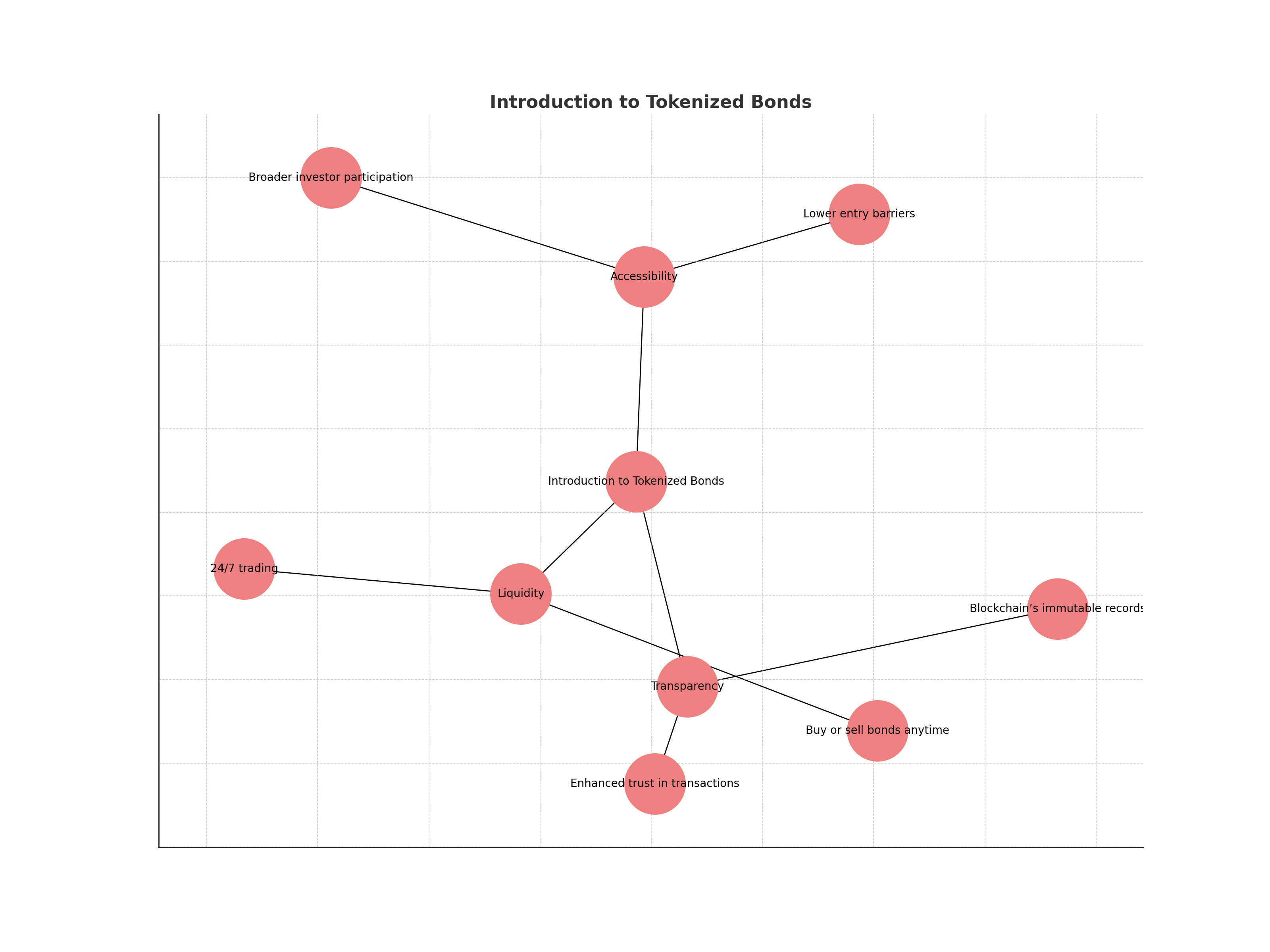
Accessibility is where tokenized bonds may have the most profound impact. Traditionally, bond markets have been dominated by institutional players due to high minimum investment thresholds and limited retail access. With blockchain technology, fractional ownership becomes possible, allowing investors to purchase smaller portions of a bond and thereby lowering the barrier to entry. According to the Bank for International Settlements, tokenized government bonds now have an average minimum investment of $110,000 compared to $185,000 for conventional bonds, a significant step toward democratizing fixed income.
Furthermore, tokenized bonds can be traded on digital platforms 24/7, vastly improving liquidity relative to their traditional counterparts. This continuous trading window enables investors to respond more nimbly to market events and manage risk with greater agility. The transparency inherent in blockchain ledgers also means that all transactions are verifiable and auditable in real time, a stark contrast to the opaque post-trade processes that still characterize much of the legacy bond market.
How Tokenized Bonds Improve Accessibility
-
Lower Minimum Investments: Tokenized bonds often require much smaller minimum investments compared to traditional bonds, enabling more individuals to participate in the bond market. For example, the Bank for International Settlements reports tokenized bonds with minimums as low as $110,000, versus $185,000 for conventional bonds.
-

24/7 Trading Access: Unlike traditional bonds, which are limited to market hours, tokenized bonds can be traded around the clock on digital platforms, offering investors greater flexibility and immediate access to liquidity. Leading platforms like LCX support continuous trading.
-

Global Investor Reach: Tokenized bonds leverage blockchain to enable borderless participation, allowing investors from various countries to access offerings without the traditional geographic or institutional barriers. Platforms such as InvestaX facilitate global access.
-
Fractional Ownership: Blockchain technology allows tokenized bonds to be divided into smaller, tradable fractions, letting investors purchase only a portion of a bond. This democratizes access and enables portfolio diversification even with modest capital. Debut Infotech highlights this as a key benefit.
The shift from paperwork to protocols isn’t just about efficiency, it’s about opening up new possibilities for global participation in fixed income markets. As more issuers experiment with blockchain rails and regulators clarify digital asset frameworks, expect secondary markets for tokenized bonds to deepen. However, liquidity is not guaranteed; it depends on both regulatory progress and widespread market adoption.
Market Adoption: What’s Next for Tokenized Bonds?
The trajectory for tokenized bonds vs traditional bonds will ultimately be shaped by how quickly market infrastructure evolves and how effectively stakeholders address regulatory and technological risks. Early adopters are already seeing benefits such as faster settlement times and reduced costs, but mainstream acceptance hinges on interoperability between blockchain networks and integration with existing custodial systems.
It’s also worth noting that as more blue-chip issuers enter the space, the credibility of digital bond offerings will rise. This could trigger a virtuous cycle: increased confidence leads to higher trading volumes, which in turn attracts more participants and enhances liquidity further.
For investors considering an allocation to bond tokens, due diligence remains paramount. Scrutinize not only the creditworthiness of the issuer but also the underlying smart contract code and platform security protocols. Ask whether secondary trading venues are regulated and whether settlement processes comply with local securities laws.
The bottom line? Tokenized bonds offer a compelling alternative for those seeking exposure to fixed income while benefiting from modern efficiencies, yet they are not without unique risks. As always in finance, transparency is your best ally; seek out clear disclosures from issuers and stay attuned to evolving regulations.







